There are no items in your cart
Add More
Add More
| Item Details | Price | ||
|---|---|---|---|
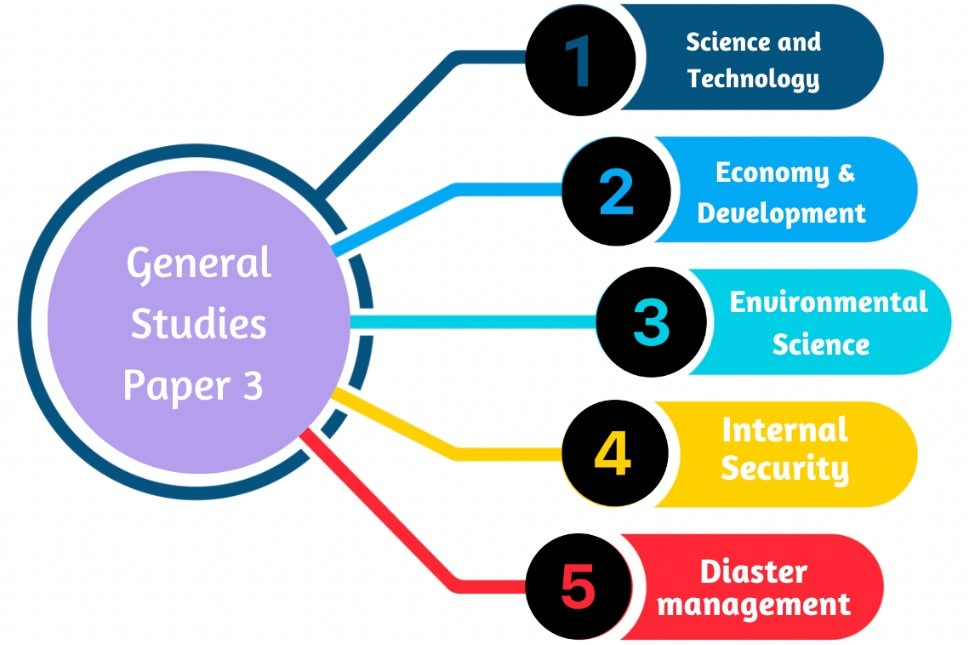
MAINS SYLLABUS
|
Geomorphology |
|
|
Climatology |
|
|
Oceanography |
|
|
Biogeography |
|
|
Human Geography |
|
|
World Geography |
|
|
Indian Geography |
|
|
Indian Physical features |
|
|
Indian River systems |
|
|
Indian Climate |
|
|
India’s Minerals and industries |
|
|
Indian Agriculture |
|
|
India’s Natural Vegetation |
|
|
India’s Economic Infrastructure |
|
|
India’s Human Geography |
|
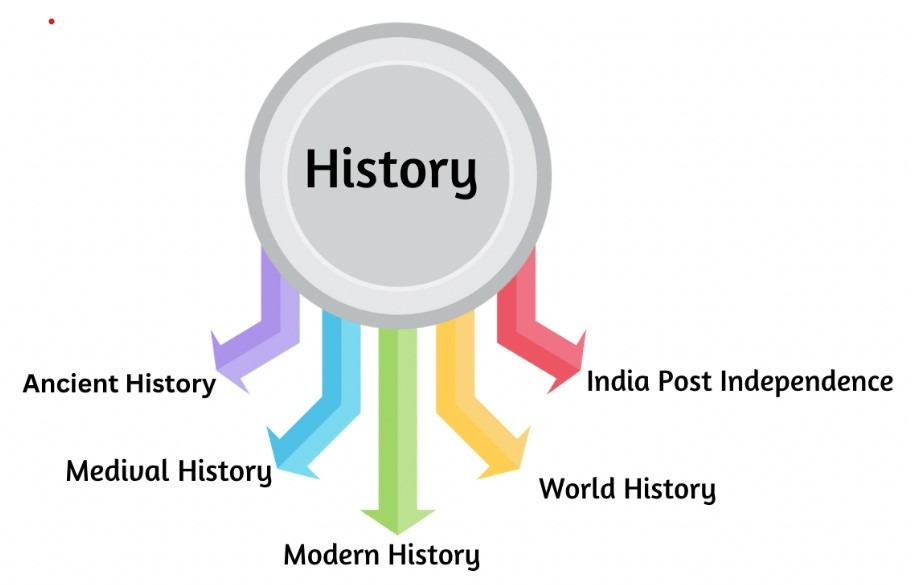
ANCIENT HISTORY
|
Pre-Historic |
Three Historical Ages:
|
|
Indus Valley Civilization (IVC) |
Here are the five areas to focus on when studying Harappan culture:
|
|
Vedic Society |
Topics on Vedic Civilization Vedic civilization:
|
|
Pre-Mauryan Period |
|
|
Jainism and Buddhism |
|
|
Mauryan Empire |
A List of Topics on the Mauryan Empire
|
|
Post-Mauryan India |
|
|
Important Modern History Events Before 1857 |
|
|
Revolt of 1857 |
The Revolt of 1857: Causes, Leaders, and Nature |
|
The Emergence of Nationalism in India during 1858-1905. |
Topics on the Unification, Education, Press, Rediscovery of India's Past, Early Political Movements, Formation of INC, and the Era of Moderates. |
|
The Rise of Militant Nationalism and Revolutionary Acts (1905-1918) |
List of Historical Events:
|
|
The Emergence of Mass Nationalism (1919-1939) |
A comprehensive list of significant events and movements that shaped India's history during the early 20th century:
|
|
Freedom and Partition (1939-1947) |
Key Events in India's Struggle for Independence from the British
|
|
The Process of Building a Nation |
|
|
Foreign Policy of India |
|
|
Economy of India After Independence |
|
|
Polity after Independence |
|
|
Social Movement After Independence |
|
|
Post-Independence Policy of Science And Technology |
|
WORLD HISTORY
|
The Emergence of the Modern World |
|
|
The First World War (WWI) |
All Events Associated with WW1 |
|
The Second World War |
All Events Associated with WW2 |
|
The Interwar Period: A Time Between Two Wars |
|
|
Redrawing National Boundaries with Decolonization in Mind |
|
|
Concept, Types & Social Impact of Political Philosophies |
|
|
Overview of Indian Art Forms |
Forms of Indian art include paintings, dances, music, puppetry, pottery, drama/theatre, martial arts, and visual art. |
|
Literature |
Indian literature across different eras and genres, including classical Sanskrit literature like the Vedas, Upanishads, and Puranas, books by Kalidasa, Vishakhadatta, and others, ancient Buddhist and Jainism literature, early Dravidian literature from the Sangam period, medieval literature, trends in medieval literature, and modern Indian literature. |
|
Architecture |
|
|
Bhakti & Sufi Movements |
|
|
|
|
Effects of globalization on Indian society, Exploring the Various Dimensions of Globalization, The forces behind globalization are multifaceted, Explore the effects of globalization on various aspects of Indian society, including socio-cultural, economic, women's rights, and the agrarian sector. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
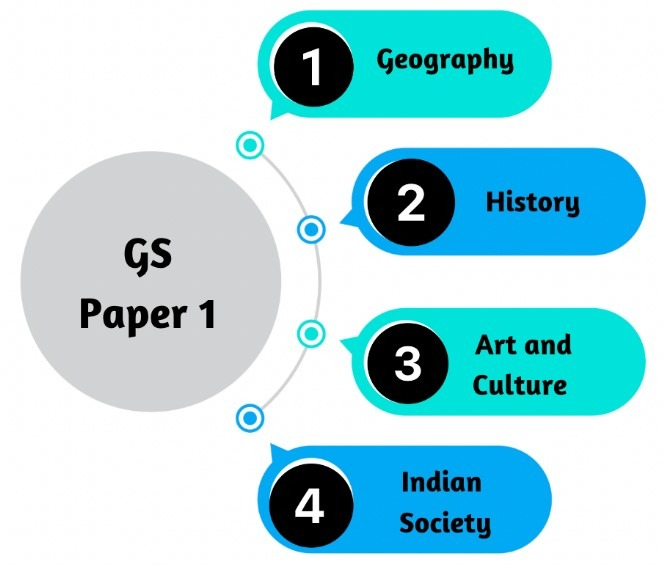
For better comprehension, it would be helpful to divide the syllabus mentioned above into distinct subjects.
|
The Historical Foundation and Evolution |
|
|
Salient Features of the Constitution |
Types of Government:
|
|
"Amendments to the Constitution" |
|
|
Key Provisions of the Constitution |
Key Components of the Indian Constitution
|
|
Functions and responsibilities of both the Union and State governments. |
|
|
Challenges and Concerns Associated with the Federal System |
Centre-State Relations Inter-State Relations Emergency and President Rule Role of Governor 2nd ARC, Punchhi, Sarkaria, etc. |
|
Devolution of powers and finances up to the local government level |
|
|
Separation of powers between various organs of the government |
|
|
Dispute redressal mechanisms and institutions |
|
|
Comparison of India’s constitutional scheme with other countries |
|
|
Structure, Organization & Functioning of the Executive, Legislators, and the Judiciary |
|
|
Appointment to Various Constitutional Posts |
|
|
Government policies and interventions for the development of various sectors |
|
|
The Connection Between Development Processes and Industry Advancement |
Non-Governmental Organizations Self Help Groups (SHGs) Societies, Trusts and Cooperatives |
|
The role of NGOs, SHGs, various groups and associations, donors, charities, institutional and other stakeholders |
|
|
Important aspects of governance, transparency, and accountability |
|
|
Social Justice |
|
|
Relations between India and neighboring countries |
India’s Bilateral relationship with
|
|
Relations between India and other countries |
India’s Bilateral relationship with USA, Russia, Japan, Korea, Europe, African Nations, Middle East, Lattin America, Australia & and New Zealand, and Pacific Countries |
|
Regional & Global Groupings |
|
|
Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India’s interests |
|
|
Indian diaspora |
The Indian Diaspora: A Global Perspective Initiatives for Engaging with India's Diaspora Policy
Role played by Indian Diaspora Issues Concerning the Diaspora |
|
Significant Global Organizations, Agencies, and Fora |
|
|
The Impact of Scientific Advancements on Daily Life and Their Practical Applications |
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) New Drugs and Therapies discovered Food-related advancements like GM Crops. Water purification and air purification. |
|
Achievements of Indians in Science & Technology |
Achievements of Indian Institutions (ISRO) Achievements of Indian Scientists Achievements of Indian Educational Institutes and other organizations. |
|
Indigenization of Technology & and Developing New Technology |
|
|
Exploring Awareness Across Different Fields |
|
|
Issues Relating to Intellectual Property Rights |
|
|
Biodiversity |
Exploring Biodiversity: Genetic, Species, Ecosystem, and More. The Significance of Biodiversity: Ecosystem Services, Economically Important Bio-Resources, and Social Benefits Loss of Biodiversity |
|
Conservation |
|
|
Environmental Pollution & Degradation |
An Overview of Pollution and Pollutants The Effects of Pollution and Degradation
Identifying the Causes and Sources of Pollution and Degradation Controlling and Preventing Pollution and Degradation Overview of National Environmental Agencies, Legislation, and Policies International Environmental Agencies and Agreements |
|
Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) |
What is an Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) Process of EIA Need & Benefits of EIA Issues with EIA |
|
|
The Correlation Between Development and the Proliferation of Extremism |
|
|
Communication Networks: A Threat to Internal Security |
|
|
The Impact of External State and Non-State Actors on Internal Security Challenges |
Non-State Actors as a Source of Threats
Institutional Framework to Tackle the Challenge of Internal Security
Factors Contributing to the Spread of Terrorism State Sponsored Terrorism |
|
Cyber Security |
|
|
Money-Laundering |
|
|
Security Challenges in Border Areas |
|
|
Organized Crime and Terrorism |
|
|
Various Security Forces & Agencies and their Mandate |
|
|
Economic Planning |
|
|
Mobilization of Resources |
|
|
Growth & Development |
|
|
Inclusive Growth |
Meaning and significance of inclusive growth. |
|
Budget |
Different Components of Budget Types of Budgets Fiscal Deficit and other type of budget Fiscal Policy of Government FRBM Act |
|
Liberalization |
The phase of Liberalization in India Cause of Liberalization in India Effects of Liberalization on the Economy |
|
Industrial Policy |
|
|
Land Reforms in India |
|
|
Infrastructure |
|
|
Investment Models |
Need for Investment Sources of Investment Models Followed by India |
|
Agriculture |
|
Detailed Syllabus of Ethics, Integrity and Aptitude
|
Ethics and Human Interface |
|
|
Human Values |
|
|
Attitude |
Content, Structure, Function; its Influence and Relation with Thought and Behaviour; Moral and Political Attitudes; Social Influence and Persuasion. |
|
Aptitude |
|
|
Emotional Intelligence |
|
|
Moral Thinkers and Philosophers |
|
|
Civil Service Values |
|
|
Probity in Governance |
Concept of Public Service; Philosophical Basis of Governance and Probity; Information Sharing and Transparency in Government, Right to Information, Codes of Ethics, Codes of Conduct, Citizen’s Charters, Work Culture, Quality of Service Delivery, Utilization of Public Funds, Challenges of Corruption. |
|
Case studies on the above-mentioned issues. |
GS Paper 4 Structure












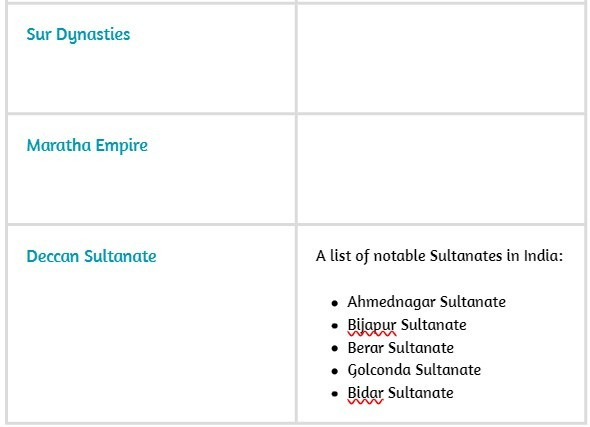









 GS Paper 2
GS Paper 2