There are no items in your cart
Add More
Add More
| Item Details | Price | ||
|---|---|---|---|
GS Paper III- Science and Technology
1. Growing seafood outside the sea
GS Paper III- Security Challenges & their Management in Border Areas
2. INS Sumitra Tackling Maritime Piracy
GS Paper II- Inter-state relations
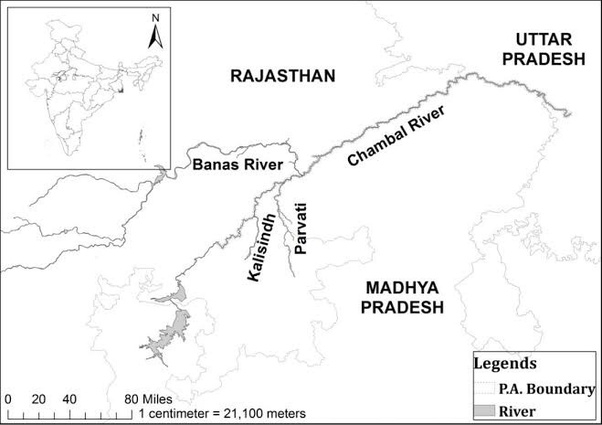
3. Parbati-Kalisindh-Chambal-ERCP (Modified PKC-ERCP) Link Project
Prelims Booster:-
4. Generative AI (genAI)
5. Earthquake sensors: seismometers
6. Matua community
7. Laughing gull
8. Students Islamic Movement of India
9. Exercise ‘SADA TANSEEQ’
10. Anti-profiteering provisions under GST
GS Paper III- Science and Technology
Context:
Kochi-headquartered ICAR-Central Marine Fisheries Research Institute (CMFRI) has entered into a collaborative research agreement with a private-sector start-up offering cultivated meat technology solutions to grow fish meat in the laboratory.
Several countries are experimenting with lab-grown fish meat to meet the increasing demand for seafood while reducing pressure on wild resources.
Overfishing has resulted in a significant reduction of certain species, impacting entire marine ecosystems.
Lab-grown fish meat has the potential to ensure food security and environmental benefits by reducing traditional fishing, being free of antibiotics and environmental contamination, and having no contact with ocean pollutants like microplastics and heavy metals.
Countries with similar initiatives:
Countries, including Israel, Singapore, the United States, and China, are making progress in lab-grown fish meat production.
Israel-based Forsea Foods successfully created lab-grown freshwater eel meat and aims to make it available in markets in the next few years.
In India, a public-private partnership between the Central Marine Fisheries Research Institute (CMFRI) and Neat Meatt aims to accelerate the development of cultured seafood.
This collaboration combines CMFRI's marine research expertise with Neat Meatt's knowledge of the field, potentially paving the way for a sustainable and secure future for seafood production in India.
The project is expected to establish proof of concept within a couple of months.
Other kinds of meats:
Lab-grown meat from cells is being developed by dozens of companies worldwide, including chicken, pork, lamb, fish, and beef.
Investment in the industry has exceeded $2.6 billion, and the Good Food Institute reports more than 150 companies operating across 6 continents.
Two California-based companies have been granted permission to sell lab-grown chicken meat in the US.
GS Paper III- Security Challenges & their Management in Border Areas
Context:
A swift response by an Indian Navy ship, INS Sumitra, deployed in the Gulf of Aden ensured that a hijack situation was quickly resolved, ensuring the safe release of an Iranian-flagged fishing vessel and its crew.
Details:
Indian Navy ship, INS Sumitra, on anti-piracy operations in the Gulf of Aden, responded to a distress message regarding the hijacking of an Iranian fishing vessel, Iman, and its crew.
INS Sumitra intercepted the vessel, coerced the pirates for the safe release of the crew and boat, and ensured the successful release of all 17 crew members.
The fishing vessel was sanitized and released for onward transit.
Piracy incidents have increased again in the region after a peak in 2010.
The Indian Navy has previously secured and safely evacuated all crew members from a hijacking attempt on a merchant vessel, Lila Norfolk.
INS Sumitra:
INS Sumitra is the fourth and final Saryu-class patrol vessel of the Indian Navy.
It was built by Goa Shipyard and designed for fleet support, coastal and offshore patrolling, ocean surveillance, and escort duties.
The vessel was commissioned on September 4, 2014, and will operate under the Eastern Naval Command to conduct maritime surveillance and coastal security missions.
Maritime Piracy:
Article 101 of the 1982 United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea defines piracy as acts of violence, detention, or depredation committed for private ends on the high seas or outside the jurisdiction of any state.
These acts are carried out with the intent of personal gain and are considered a serious maritime crime subject to international laws and conventions.
The strongest zones of pirate activity include the Gulf of Guinea, the Horn of Africa, the Red Sea, the Indian Ocean, Southeast Asia, and the Indian subcontinent.
Gulf of Aden:
The Gulf of Aden is situated between Yemen and Somalia.
It is an important waterway for transporting Persian Gulf oil.
It connects the Red Sea to the Arabian Sea via the Strait of Bab el Mandeb and supports rich marine life and fishing towns.
Major ports in the region include Aden and Djibouti. However, the Gulf has also received attention due to piracy, terrorism, and refugee smuggling in recent years.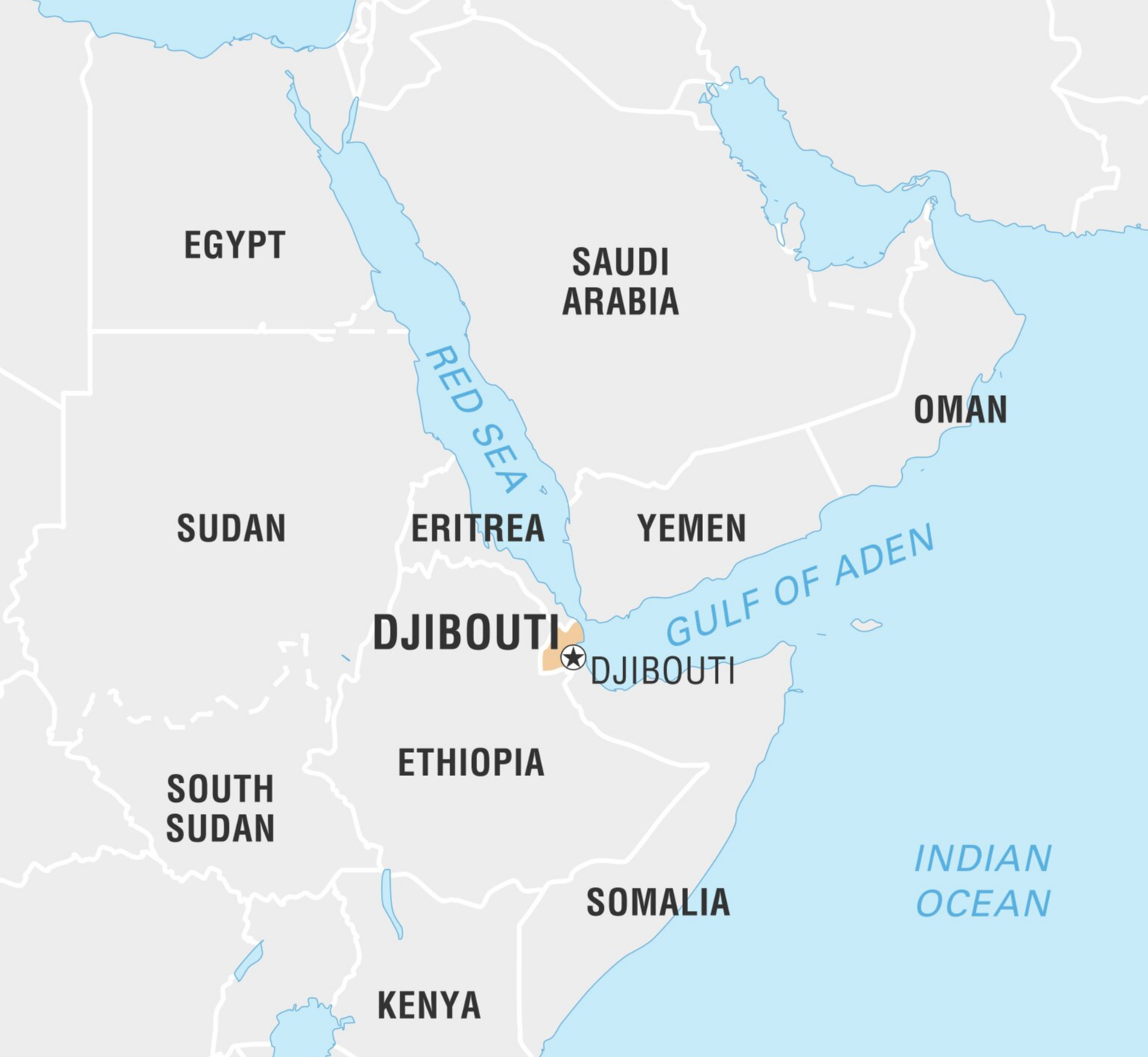
Related Search:
Operation Prosperity Guardian
SAGAR policy
Indian Ocean Rim Association
GS Paper II- Inter state relations
Context:
Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with the Union Ministry of Jal Shakti to implement the Modified Parbati-Kalisindh-Chambal-ERCP (Modified PKC-ERCP) Link Project.
Context:
A new report predicts that Generative AI (genAI) is poised to become a $100 billion industry by 2026.
Generative AI:
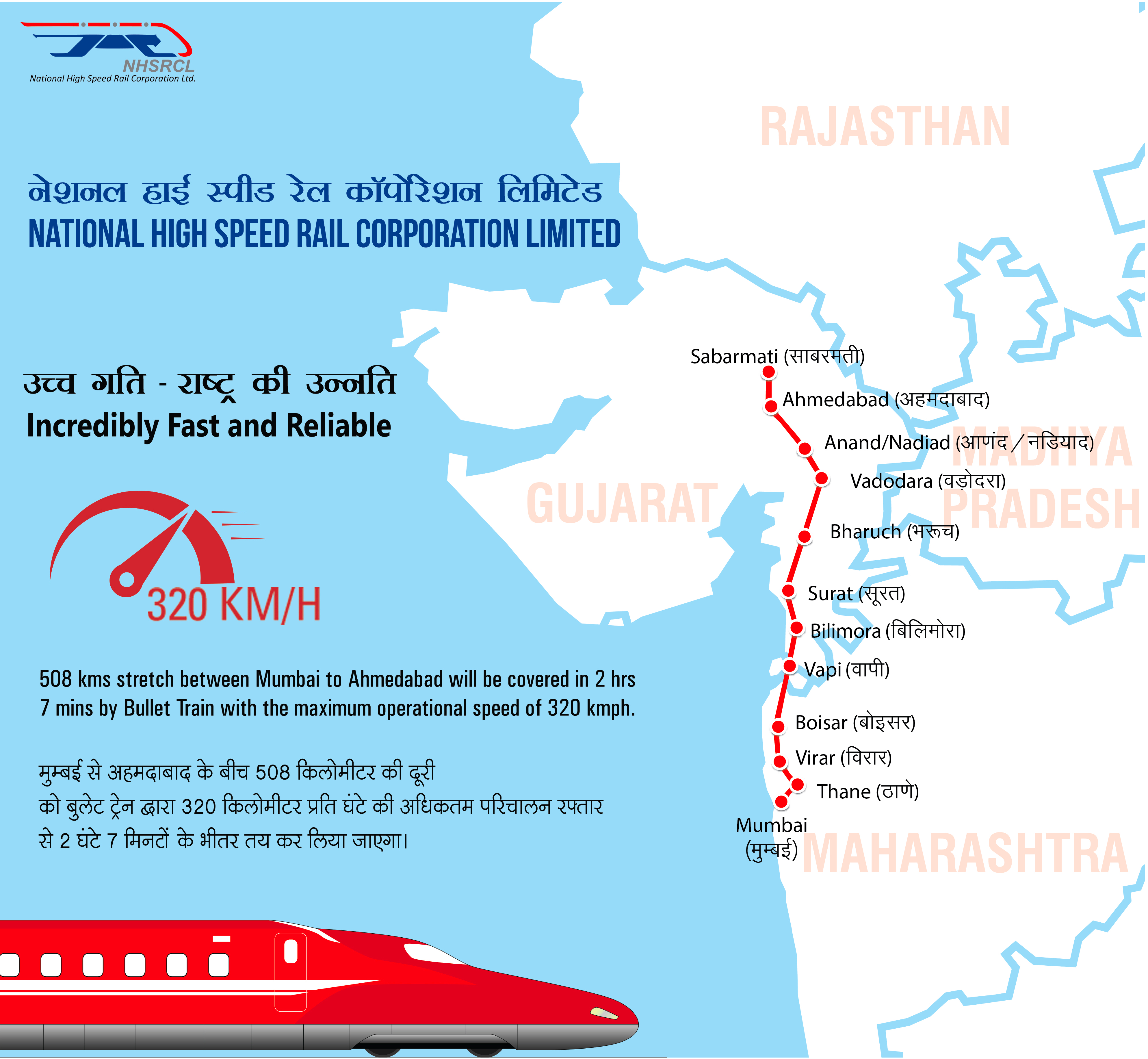
Context:
Twenty-eight seismometers will be installed along the proposed bullet train route between Mumbai and Ahmedabad.
Context:
Union Minister Shantanu Thakur reiterated that the Citizenship (Amendment) Act (CAA) would be implemented across the country in a week.
Context:
Laughing gull, a migratory bird from North America, has been sighted for the first time in the country at the Chittari estuary in Kasaragod district (Kerala).
Laughing gull:
The Atlantic Laughing Gull is a unique species known for its laughter-like calls, which resemble human laughter.
This medium-sized gull has fairly long wings and legs that impart a graceful look when they are flying or walking.
They also have stout, fairly long bills.
The Atlantic Laughing Gull is an opportunistic carnivore and scavenger.
They eat a variety of foods including fish, shellfish, crabs, molluscs, insects, bird eggs, and young birds.
It takes 2-3 years for the Atlantic Laughing Gull to gain adult plumage.
They are graceful and charming birds that are a delight to watch.
Habitat and Distribution:
These coastal birds are mainly found on the Atlantic coast of North America, the Caribbean, and northern South America.
They are only occasionally seen very far inland.
Conservation Status:
According to the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), the Atlantic Laughing Gull is of least concern.
Context:
The Union Home Ministry has extended the ban on the Students Islamic Movement of India (SIMI) for five years.
Reasons:
The organisation was declared an “unlawful association” under the Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act for the first time in 2001.
SIMI has been found involved in fomenting terrorism, disturbing peace and communal harmony to threaten the sovereignty, security and integrity of Bharat.”
17 cases had been registered against former SIMI cadres in the past five years and in 11 instances, SIMI members had been convicted by courts of law for various crimes committed between 2006 and 2014.
About Students Islamic Movement of India:
The Students' Islamic Movement of India (SIMI) is a proscribed terrorist organization that originated in Aligarh, Uttar Pradesh, in April 1977.
SIMI's avowed objective is the ‘liberation of India’ to transform it into an Islamic state.
The organization has declared Jihad against India, seeking to establish Dar-ul-Islam (land of Islam) through either coerced conversion to Islam or through acts of violence.
Officially designated as a terrorist outfit by the Indian government, SIMI was banned in 2001, shortly after the 9/11 attacks.
In February 2019, the Government of India extended the ban on SIMI for an additional five years, commencing from February 1, 2019, under the Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act.
Context:
The inaugural edition of the India-Saudi Arabia Joint Military Exercise ‘SADA TANSEEQ’ commenced at Mahajan, Rajasthan.
Context:
The Delhi High Court recently upheld the constitutional validity of anti-profiteering provisions in the Goods and Services Tax (GST).
What are Anti-Profiteering provisions under GST?
Under the anti-profiteering provisions of GST, any reduction in the GST rate or benefit of input tax credit must be passed on to the end consumer.
It is illegal for businesses to retain these benefits and indulge in illegal profiteering.
The Anti-Profiteering Rules, 2017 (defined under Section 171 of the Central Goods and Services Tax Act 2017) regulate anti-profiteering.
The National Anti-Profiteering Authority (NAA) is responsible for finding and taking action against taxable registered persons who engage in illegal profiteering.
The NAA has the power to determine the methodology and procedure for identifying such persons.