There are no items in your cart
Add More
Add More
| Item Details | Price | ||
|---|---|---|---|
GS Paper II- Statehood relations
1. Ladakh’s demand on Gilgit-Baltistan
GS Paper II- Indian Constitution– historical underpinnings, amendments, significant provisions
2. Sapinda marriages
GS Paper II- Indian Constitution– historical underpinnings, evolution, features, amendments, significant provisions and basic structure.
3. Uttarakhand Uniform Civil Code
Prelims Booster
4. Nitrogen hypoxia
5. Western Equine Encephalitis Virus
6. Nepal & China to sign BRI implementation
7. Dogri folk dance
GS Paper II- Statehood relations
Context:
Ladakh’s two key socio-political conglomerates as part of an ongoing dialogue between the Centre and the newly-carved Union Territory demand for extending of the territorial control of Ladakh up to Gilgit-Baltistan in Pakistan-occupied Kashmir.
Current Status of Ladakh:
Ladakh, a Muslim-majority Union Territory, was created out of the Kashmir division of the State of Jammu and Kashmir in August 2019 when the special constitutional position of the region provided under Article 370 was ended.
It is governed by two elected hill councils, LAHDC-Kargil and LAHDC-Leh, with a population of 2.74 lakh.
The region witnessed a divided reaction to the Centre’s moves to abrogate Article 370 and 35A, with Leh supporting the demand for UT status, while Kargil insisting on reunification with Kashmir.
Latest demands of the region:
The people of Leh and Kargil are protesting for the restoration of Statehood with a legislature, and for special status under the Sixth Schedule and Article 371 of the Indian Constitution.
They argue that opening the region to outsiders and outside investment will impact ecologically fragile and sensitive areas.
Ladakh also demands exclusive rights over recruitment and the establishment of the Ladakh Public Service Commission for gazetted jobs.
It also calls for the Twin Hill councils to have the power to recruit lower-rung staff and for the Ladakh resident certificate to be the only basis for applying for jobs in the region.
Reason of Territorial Extension:
A memorandum from Ladakh district in India seeks to extend territorial control up to Gilgit-Baltistan, which is now occupied by Pakistan.
It demands reservation of seats for Gilgit-Baltistan and emphasizes the importance of empowering locals for stability in the region.
Ladakh shares a Line of Actual Control with China and saw a violent skirmish in 2020.
The memorandum highlights the usefulness of locals' understanding of the harsh terrain in military and logistic operations.
Centre's Stand:
In 2022, a committee was formed by the Centre to address the concerns of the people of Ladakh.
However, it failed to arrive at a solution, leading to more protests in 2023.
Another committee was formed in 2023 to engage with the stakeholders of Ladakh.
In 2024, these bodies submitted a written memorandum to pave the way for more structured talks between New Delhi and Ladakh over the list of demands.
Location of Gilgit Baltistan:
It is bordered by China in the North, Afghanistan in the west and Kashmir in the southeast.
The China-Pakistan Economic Corridor passes through this region.
The territory of present-day Gilgit-Baltistan became a separate administrative unit in 1970 under the name “Northern Areas”.
The territory of Gilgit-Baltistan is highly mountainous. 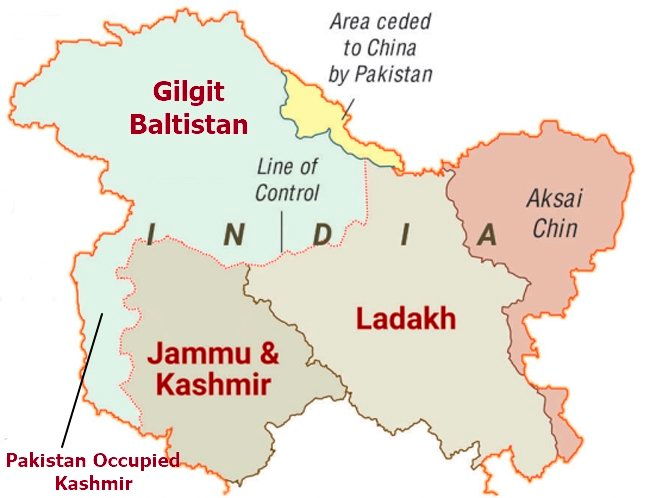 .
.
Related Search:
About K2
UNCIP
CPEC
Prelims Specific:
Gilgit-Baltistan- Location, neighbours and important rivers flowing through.
What is the Karachi Agreement related to?
The 1963 Pak- China Boundary Agreement.
1972 Simla Agreement.
About PoK and CPEC.
GS Paper II- Indian Constitution– historical underpinnings, amendments, significant provisions
Context:
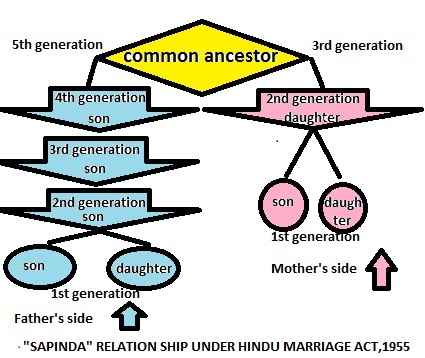
Delhi High Court rejected a challenge to the constitutionality of Section 5(v) of the Hindu Marriage Act, 1955 (HMA), which prohibits marriage between two Hindus if they are “sapindas” of each other.
In some European countries, incest laws are less strict than in India.
In France and Belgium, incest was decriminalized in the 1810 Penal Code, and despite Belgium introducing a new code in 1867, incest remains legal.
Portugal also does not criminalize incest.
In Ireland, while same-sex marriages have been recognized since 2015, incest laws have not been updated.
Italy considers incest a crime only if it causes a "public scandal."
In the United States, incestuous marriages are prohibited in all states, but relationships between consenting adults are allowed in New Jersey and Rhode Island.
Related Search:
Hindu Marriage Act
Muslim Personal law
Prelims Specific:
About Sapinda marriage
Provision under the Hindu Marriage Act
Exceptions to the prohibition against Sapinda marriages
Grounds of Challenge to Sapinda
Similar laws in other countries
GS Paper II- Indian Constitution– historical underpinnings, evolution, features, amendments, significant provisions and basic structure.
Context:
On February 5, the Uttarakhand Assembly will convene to pass the Uniform Civil Code (UCC) Bill.
Background/History:
The Government promised to introduce a Uniform Civil Code (UCC) for all religions during the 2014 general elections in India.
The UCC would govern personal laws related to marriage, inheritance, divorce, and adoption.
The party reiterated this promise before the 2022 state Legislative Assembly elections in Uttarakhand.
Following their electoral victory, the Uttarakhand government announced a committee led by former Supreme Court Judge Ranjana Prakash Desai would submit a report with a draft of the Bill.
The UCC faced opposition from rival political parties.
The committee received over 2.5 lakh suggestions from the public and held 38 public meetings across the state.
It has completed its work and is ready to be submitted ahead of the 2024 general elections.
Expected Changes:
The Uttarakhand government has released a report that emphasizes gender equality in the Uniform Civil Code (UCC), including uniform personal laws for all residents of the state and equal inheritance rights for men and women.
The UCC will also reject polygamy, iddat, and halal practices, and regulate live-in relationships with mandatory declarations for starting and ending the relationships.
The minimum age for marriage will remain the same.
Following states:
After the implementation of the UCC in Uttarakhand, similar bills are expected in Gujarat and Assam.
A committee was formed in Gujarat, and the Assam Chief Minister expressed support for the UCC.
Goa was the first state to implement the UCC.
Uniform Civil Code (UCC)-:
The Uniform Civil Code (UCC) calls for the formulation of one law for India, which would apply to all religious communities in matters such as marriage, divorce, inheritance, and adoption.
Article 44: The “State shall endeavour to provide for its citizens a uniform civil code (UCC) throughout the territory of India.”
The Uniform Civil Code (UCC) was included in the Directive Principles.
Related Search-:
Difference btw Fundamental Rights and DPSP.
Art- 25, 14, 44, 21.
Prelims Specific-:
what is UCC
its origin.
Why do we need UCC?
Significance and challenges
Context:
Alabama inmate Kenneth Smith was executed by nitrogen hypoxia, marking the United States’ first execution using the method.
A "NIOSH-approved Type-C full facepiece supplied air respirator" was used to deliver pure nitrogen gas in an execution, depriving the body of oxygen and causing death.
While nitrogen is harmless in normal conditions, breathing in pure nitrogen deprives the body of oxygen needed to maintain bodily functions.
The death would occur within minutes after inhaling nitrogen gas.
Nitrogen hypoxia is a method of execution that replaces oxygen with nitrogen, ultimately leading to the death of an individual.
The International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR) marked the beginning of global efforts for the abolition of the death penalty, despite its prevalent use in many countries during the early 1960s.
Critics have referred to it as "human experimentation."
Nitrogen:
Nitrogen gas, which is colourless and odourless, is a major component of the atmosphere.
Plants require nitrogen to grow, which can be 'fixed' by lightning or added to soil in the form of fertilizers.
The chemical industry relies heavily on nitrogen gas, which is used to produce a variety of products, including fertilizers, nitric acid, nylon, dyes, and explosives.
It is also used to provide an unreactive atmosphere, preserving foods and contributing to the production of transistors and diodes in the electronics industry.
Annealing, a heat treatment that makes steel easier to work, requires large quantities of nitrogen.
Liquid nitrogen, which is often used as a refrigerant, can rapidly freeze foods, helping to maintain moisture, colour, flavour, and texture.
Context:
Argentina alerted the Pan American Health Organization/World Health Organization (PAHO/WHO) of a human case of Western Equine Encephalitis Virus (WEEV) infection.
Western Equine Encephalitis (WEEV):
The Western Equine Encephalitis Virus (WEEV) is a virus that is transmitted through mosquitos and belongs to the Togaviridae family of viruses.
The virus consists of a single-stranded RNA genome that is approximately 11.5 kilobases long.
The WEEV is a hybrid of the Eastern Equine Encephalitis Virus (EEEV) and a Sindbis-like virus.
Passerine birds are believed to be the virus's reservoir, while equine species act as intermediate hosts.
Mosquitoes are the primary vector that spreads the virus to humans.
Its Symptoms:
Although the majority of cases show no symptoms, some people may experience severe consequences as a result of this infection.
In about 4-5% of cases, the infection may cause inflammation in the brain, leading to neurological symptoms and complications.
Unfortunately, there is no specific antiviral treatment available for this condition.
Therefore, providing symptomatic care is extremely important, particularly for those experiencing neurologic symptoms.
Context:
Nepal and China will sign the implementation plan of the Belt and Road Initiative “very soon”.
- Nearly seven years after the two neighbours inked an agreement to undertake ambitious Beijing-backed infrastructure projects in the Himalayan nation.
Major Highlights:
Nepal and China signed a Memorandum of Understanding on the BRI in 2017.
However, not a single project under the initiative, a pet project of Chinese President Xi Jinping, has either been executed or negotiated.
The BRI, which aims to enhance connectivity and promote economic cooperation, has opened up new avenues for collaboration between the two nations
Belt and Road Initiative (BRI):
The Belt and Road Initiative is a massive international development and infrastructure project launched by China in 2013.
It encompasses two main components: the Silk Road Economic Belt and the 21st Century Maritime Silk Road.
The "Belt" refers to a network of overland corridors that connect China to Europe via Central Asia and the Middle East, while the "Road" refers to a maritime route connecting China to Southeast Asia, South Asia, Africa, and Europe.
The BRI aims to promote economic cooperation, trade, and development across these regions through the construction of transportation infrastructure, energy projects, and various forms of economic and cultural exchanges.
The initiative has been met with both enthusiasm and criticism, with concerns raised about debt sustainability, transparency, and geopolitical implications.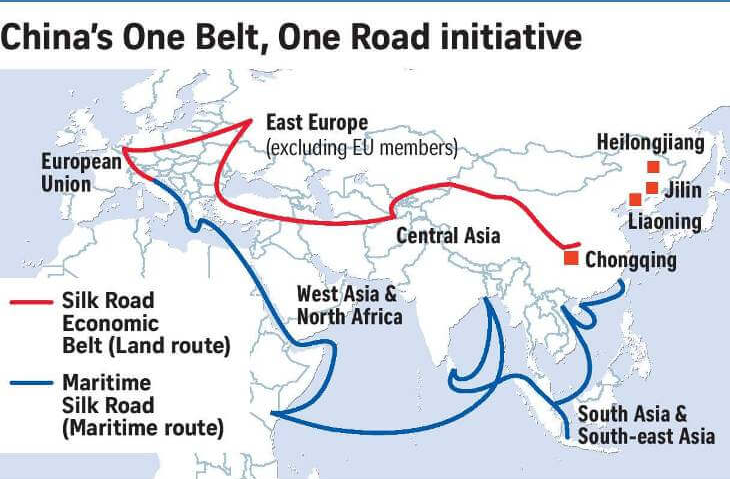
Context:
The Union government conferred Padma Shri awards to Jammu Dogri folk dancer Romalo Ram, Srinagar woodcarver Ghulam Nabi Dar and Shimla vocalist Som Dutt Battu.
About Dogri folk dance: