There are no items in your cart
Add More
Add More
| Item Details | Price | ||
|---|---|---|---|
GS Paper 2: Important International institutions, agencies
Context-:
Amid Israel’s ongoing military attacks on the Gaza Strip, particularly in its southern region, United Nations Secretary-General Antonio Guterres has invoked Article 99 of the UN Charter in a bid to establish a ceasefire.
Guterres' Invocation:-
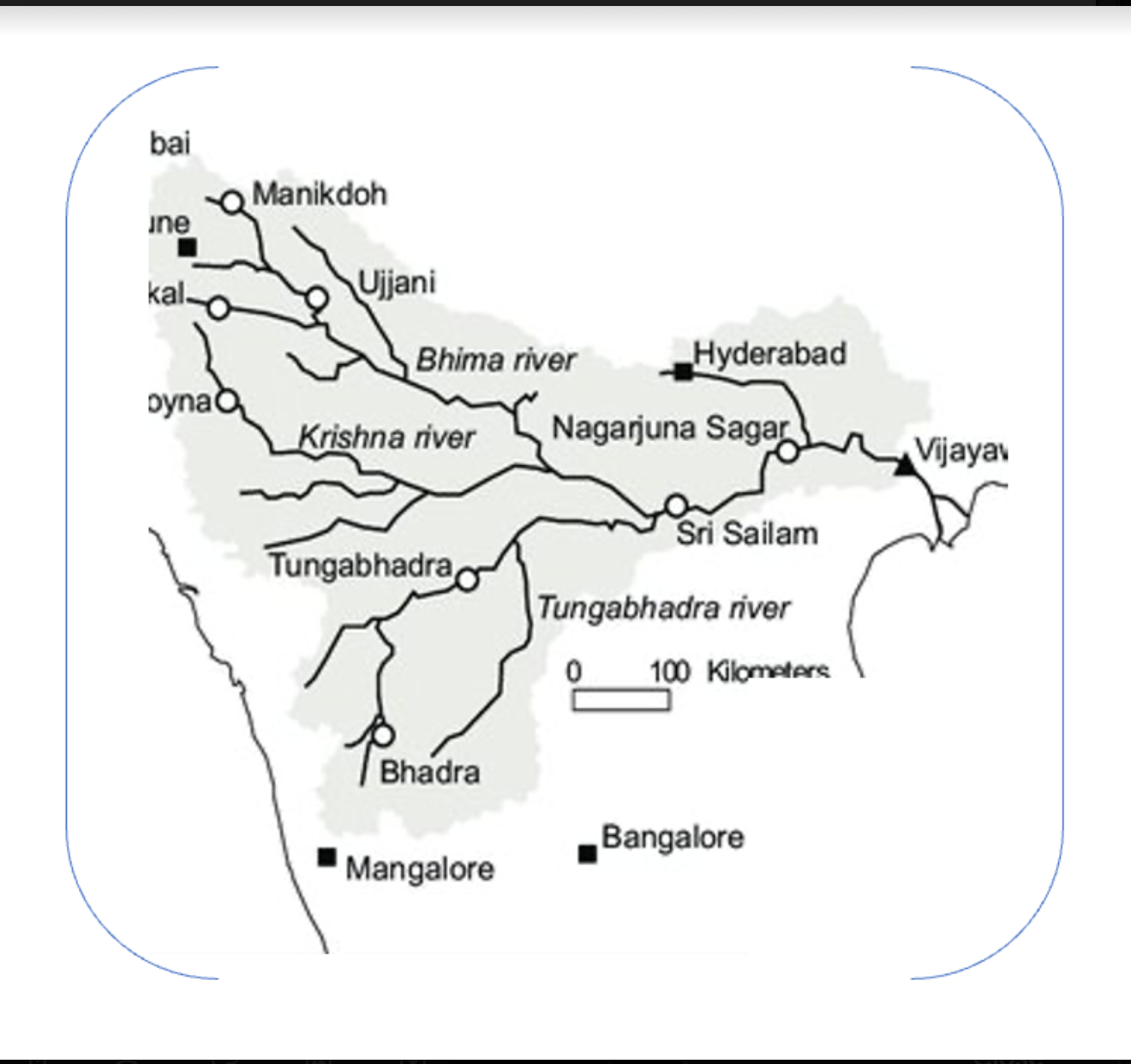
GS Paper 3: Inter-State Relations & Water Resources
Context-:
The dispute over the sharing of the Krishna River waters between Andhra Pradesh and Telangana had come to the fore once again.
GS Paper 2: Structure, organization and functioning of the Executive and the Judiciary.
Context-:
The ethics committee of the Lok Sabha is believed to have recommended the expulsion of Trinamool Congress Member of Parliament (MP) Mahua Moitra from the Lok Sabha for her “unethical conduct” and “breach of privileges”.
Details-:
This follows the ethics committee examining the complaints which accused her of asking questions to target a leading business house at the behest of a businessman in exchange for cash.
She was also accused of sharing her login credentials with the businessman.
Role of Ethics Committee:-
Context-:
The 24th edition of Hornbill Festival, an annual extravaganza in Nagaland, kicked off on December 1 and is set to conclude on December 10.
Details-:
Chief Minister Neiphiu Rio announced the participation of an American music band.
International support with partnerships from the US, Germany, and Colombia.
Jointly organized by state tourism and art & culture departments.
Venue: Naga Heritage Village, Kisama, around 12 km from Kohima.
Primary objective: Revive and safeguard Nagaland’s cultural traditions across all tribes.
About Hornbill-:
Context-:
The government announced a new project in the Rajya Sabha aimed at highlighting the cultural richness of villages across the nation.
Details-:
Developed in partnership with the Indira Gandhi National Centre for the Arts (IGNCA) under the Ministry of Culture.
The initiative, known as "Mera Gaon, Meri Dharohar", seeks to explore the life, history, and ethos of Indian villages.
As a crucial component of the National Mission on Cultural Mapping, the project reflects the central government's commitment to document and map the cultural diversity inherent in villages across the country.
Objective-:
The main objective of the project is to culturally map India's 6.5 lakh villages, spanning 29 States and 7 Union Territories, on a comprehensive virtual platform.
Through MGMD, people will get an opportunity to immerse themselves in the diverse and vibrant cultural heritage of India.
The core idea behind this project is to encourage appreciation for India's culture and traditions, paving the way for economic growth, social harmony, and artistic development in rural communities.
Categories-:
The collected information is categorized into seven broad categories:
1. Arts and Crafts Village
2. Ecologically Oriented Village
3. Scholastic Village Linked with Textual and Scriptural Traditions of India
4. Epic Village linked with Ramayana, Mahabharata, or Puranic legends and oral epics
5. Historical Village linked with Local and National History
6. Architectural Heritage Village
7. Any other characteristic that may need highlighting such as fishing village, horticulture village, shepherding village, etc.
Context-:
NITI Aayog unveils inaugural delta ranking for aspirational blocks program.
Details-:
Tiriyani Block of Kumuram Bheem Asifabad district in Telangana has emerged as the frontrunner in the first delta ranking of the Aspirational Blocks Programme (ABP) unveiled by NITI Aayog in June 2023.
The second position was secured by Kaushambi Block in Kaushambi District, Uttar Pradesh, as per a statement released by NITI Aayog.
Aspirational Blocks Programme (ABP)-:
Launched on January 7, 2023, the ABP aims to enhance governance and improve the quality of life for citizens in the most challenging and relatively underdeveloped blocks across India.
Approximately 500 blocks from 329 districts across 27 states and 4 Union Territories are part of this program.
The rankings were determined based on the performance and progress of the blocks in achieving key performance indicators (KPIs).
This KPI-centric approach is integral to the program's core strategy, fostering a sense of competitive and cooperative federalism.
In consultation with various stakeholders, 40 key performance indicators (KPIs) were chosen to measure the progress of the blocks which have been grouped into 5 themes.
Significance-:
The block rankings under the aspirational blocks program and the aspirational district program provide a valuable tool to assess progress in governance improvement and enhanced quality of life in underdeveloped regions of India.
By pinpointing areas of strength and opportunities for improvement, these rankings foster healthy competition and collaboration among states and districts, ultimately contributing to the nation's overall development.
Context-:
At the ReWired Summit at COP28 Dubai, the official launch of Green Rising took place—a platform aiming to empower youth-led climate actions and solutions.
Details-: