There are no items in your cart
Add More
Add More
| Item Details | Price | ||
|---|---|---|---|
GS Paper 3: Climate Change; Climate Financing
Context-:
The UAE, hosting COP28, pledged $30 billion for a fund to channel private sector funds into climate initiatives and enhance financing for the Global South.
Objective-:
The fund was “specifically designed to bridge the climate finance gap” and stimulate further investment of $250 billion by 2030.
What is climate finance?
Climate finance refers to large-scale investments required for actions aiming to mitigate or adapt to the consequences of climate change.
Adaptation-:
Adaptation involves anticipating the adverse effects of climate change and taking appropriate action to prevent or minimize the damage it can cause.
One example of adaptation measures includes building infrastructure to protect coastal communities against sea-level rise.
Mitigation-:
Mitigation involves reducing the emission of greenhouse gases (GHG) into the atmosphere so that the impacts of climate change are less severe.
Mitigation is done by increasing the share of renewable energy sources, expanding forest cover, etc.
Why Climate Finance -:
GS Paper 2: Governance/Social Justice
Context-:
The National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) released its annual report on crime in India for the year 2022.
The states/ UTs reporting the highest chargesheet rate under IPC crimes are Kerala (96.0%), Puducherry (91.3%), and West Bengal (90.6%).
Key Highlights-:
Registered crimes in 2022: 58,24,946, consisting of 35,61,379 IPC crimes and 22,63,567 SLL crimes.
Decline of 4.5% compared to 2021, the second pandemic year.
Crime rate per lakh population: Reduced from 445.9 (2021) to 422.2 (2022).
A more reliable indicator, considering population growth.
Cases of crime against women: 4,45,256, a 4% increase from 2021.
Dominant categories: 'Cruelty by Husband or His Relatives' (31.4%), 'Kidnapping & Abduction of Women' (19.2%), and 'Assault on Women with Intent to Outrage her Modesty' (18.7%).
Cybercrime reporting surged by 24.4 percentage points to 65,893 cases.
Primary categories: Fraud (64.8%), extortion (5.5%), sexual exploitation (5.2%).
Suicides reported: 1,70,924, marking a 4.2% increase from 2021.
Leading causes: 'Family Problems (other than marriage-related problems)' (31.7%), 'Marriage Related Problems' (4.8%), and 'Illness' (18.4%).
The male-to-female ratio of suicide victims: is 71.8:28.2.
About NCRB-:
The NCRB was established in January 1986 as a body mandated to compile and keep records of data on crime.
It also acts as a “national warehouse” for the fingerprint records of Indian and foreign criminals, and assists in locating interstate criminals through fingerprint search.
NCRB Reports-:
NCRB follows this rule, where the most severe crime in a single FIR is considered the counting unit.
Example: 'Murder with Rape' counted as 'Murder,' leading to potential undercounting of rape.
NCRB report relies on data submitted at the local level.
Inefficiencies or gaps in local data impact report accuracy.
NCRB acknowledges that socio-economic factors influencing crimes are not captured.
The underlying reasons for crimes may not be reflected in the report.
Certain groups may not report cases due to fear of an uncooperative or hostile police response.
A shortage of police officers or unfilled vacancies at the local level may hinder data collection.
Related Search-:
Crime Against Woman
Crime Against SC and ST
Prelims Specific-:
About NCRB
About NCRB Crime Report
Key Highlights
Challenges
GS Paper 3: Food processing and related industries
Context:
A groundbreaking report from the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organisation (FAO), published earlier this month, has laid bare the staggering hidden costs of our global agrifood systems.
Crops being favoured-:
Food Corporation of India (FCI) coordinates food crop procurement.
FCI heavily favours rice and wheat, procuring 341.32 lakh MT of wheat and 514.27 lakh MT of rice in 2019-2020.
Policies favouring crops like sugarcane and areca nut through investments in irrigation have thrived.
Fluctuations in global soya prices between 2012 and 2016 negatively affected income for soy farmers and agro-companies in Malwa.
Historical global trade relations influenced food production in the Global South, as seen in the pre-independence era's tax systems for enforced exports of primary raw materials like cotton.
Way Forward (Crop diversification)-:
The transition from local to global food chains is necessary to address systemic issues.
Local initiatives, like farm diversification, could be pivotal in initiating change.
Agroecology-based diversified multi-cropping systems, like 'akkadi saalu' in Karnataka, integrate various crops, trees, and livestock, rejuvenating degraded land.
Challenges and Potential-:
GS Paper 3: Major crops cropping patterns
Context:
The lower Cauvery delta was known for its cultivation of rice and agricultural surplus has declined as a hub of rice cultivation.
Decline in Delta's Rice Cultivation-:
Survey data from 2018-2019 reveals a decline in the delta's prominence as a rice cultivation hub.
It is attributed to reduced water availability due to altered water-sharing arrangements between Karnataka and Tamil Nadu.
From a double-cropped to a single rice-crop region during the 'green revolution,' it reverted to a single-crop status with decreased rice yields in Palakurichi village.
Reasons for Crop Pattern Changes-:
Apart from erratic Cauvery water supply, unaddressed agricultural policies aggravated the shift in crop patterns.
Lack of suitable crops for altered water availability and outdated irrigation systems contributed to this change.
Recurring droughts (2000-2002, 2008, 2012, 2016) and Cyclone Gaja's impact in 2018 emphasized the need for adapted agricultural policies.
Absence of Economic Diversification-:
Despite the decline in green revolution gains, no significant alternative economic activities emerged in the surveyed villages, aside from rice production.
The region lacks new sources of economic activity, indicating a heavy reliance on rice cultivation without diversification.
Social Differences-:
- It's named 'Ponni' in Tamil and holds a revered status as a river in southern India.
- Originating from the Brahmagiri Hill in southwestern Karnataka.
- It courses southeastward through Karnataka and Tamil Nadu, culminating its journey by cascading through the Eastern Ghats before emptying into the Bay of Bengal near Pondicherry.
- Left Bank Tributaries:- include Arkavathi, Hemavathi, Shimsa, and Harangi.
- Right Bank Tributaries:- encompass Lakshmantirtha, Suvarnavati, Noyil, Bhavani, Kabini, and Amaravathi.
About Cauvery Delta-:
The Cauvery delta region is an important agricultural region in Tamil Nadu.
It has been seen that in the last four decades, Tamil Nadu’s food dependence on the delta has fallen from 65% to 40%.
Hydrocarbon wells are one of the major reasons behind the same.
This deltaic region is renowned for its rich alluvial soil and a network of irrigation canals that support extensive agriculture, especially the cultivation of rice and other crops.
The delta has a unique cultural heritage, with its historical significance reflected in ancient temples, art, and literature. 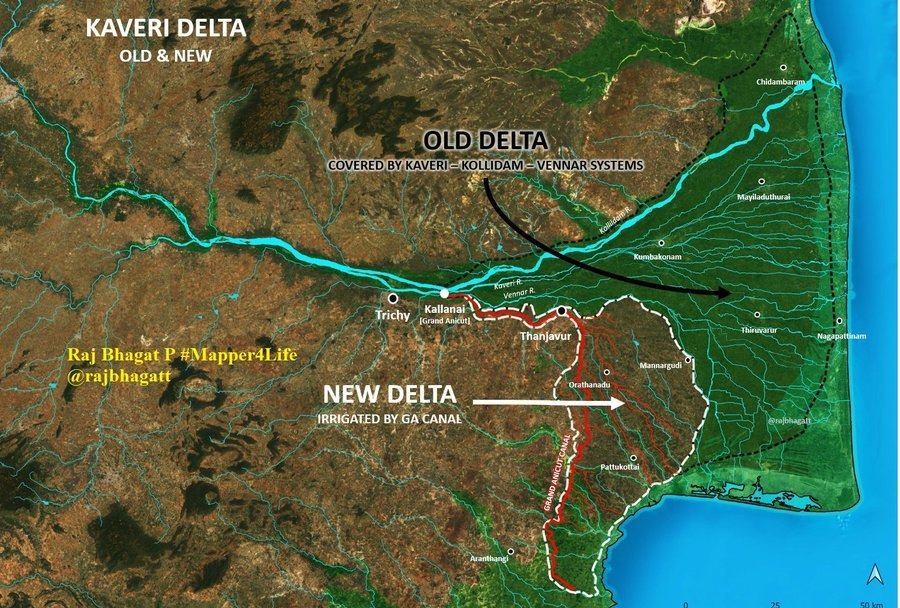
Related Search:
Cauvery water dispute
Cauvery River
Prelims Specific:
Specific crop of Cauvery delta
Reason for Decline in Delta's Rice Cultivation
Social Differences in Cauvery delta cultivation
About River Cauvery (Kaveri), Cauvery Delta
GS Paper 2 & 3: Environmental Pollution and degradation, Climate change, Government Plan and Policies
Context:
India has refused to sign the COP28 Declaration on Climate and Health, due to the lack of practicality in curbing greenhouse gases used for cooling in the health sector, as the reason.
India has said that it would not be possible to fulfill the same within the short term.
India's Concern-:
Context:
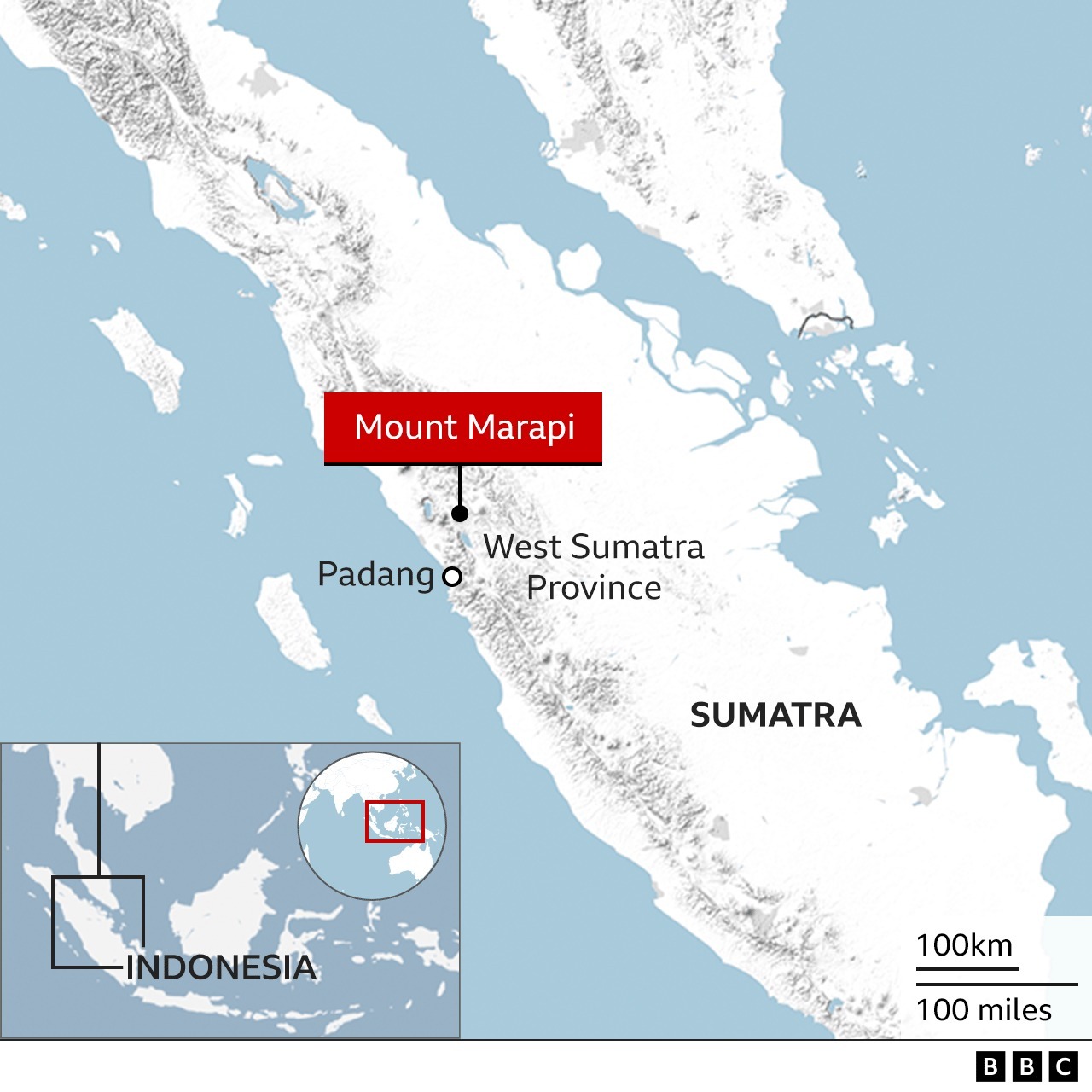
Indonesia’s Mount Marapi in West Sumatra province erupted, spewing white-and-grey ash plumes for more than 3,000 meters (about 9,800 feet) into the air.
Details-:
Context-:
Hackers are now using a phony browser update chain identified as "ClearFake" to infect Mac users with AMOS.
Details-:
Researchers identified Atomic macOS Stealer (AMOS), a sophisticated virus that primarily targets Apple users, as a new cyber threat at the beginning of 2023.
The AMOS malware can retrieve private data from a victim's device once it has been installed.
This data can include credit card numbers, cryptocurrency wallet passwords, iCloud Keychain passwords, and other files.
What is ClearFake-:
ClearFake is a kind of deepfake that is created by using machine learning to manipulate images or videos in a way that makes them appear real.
It can be done by using several techniques such as image splicing, facial recognition and voice synthesis.
How clear fake is a threat-:
Context-:
African leaders came together at the 28th COP28 of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change to launch the green industrialization of the continent.
The initiative aims to position Africa as a global supplier of green energy and resources.
Details-: