There are no items in your cart
Add More
Add More
| Item Details | Price | ||
|---|---|---|---|
GS Paper 3: Achievements of Indians in science and technology; indigenization of technology, Awareness in the fields of Space.
Context:
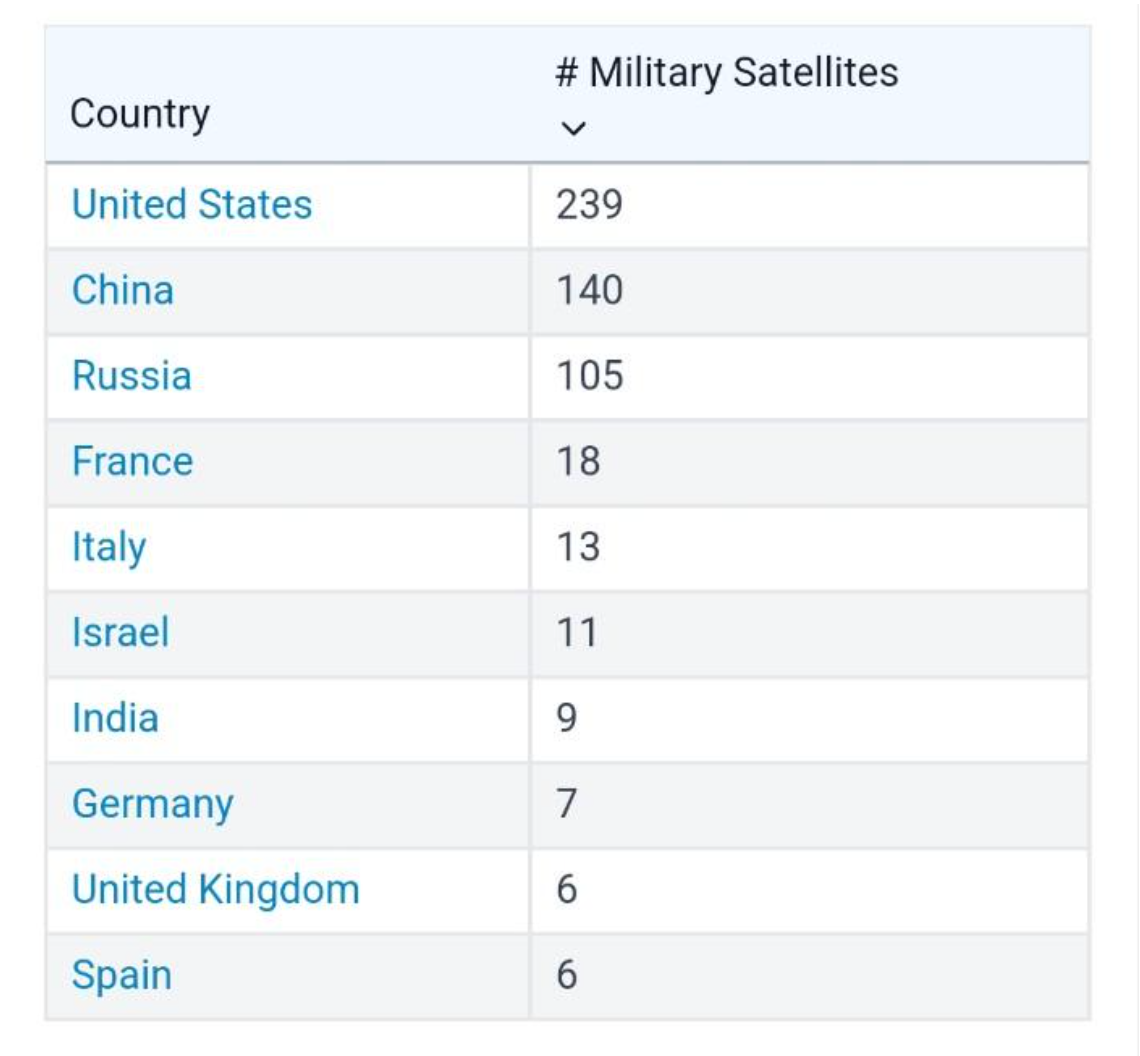
At `Techfest', an annual science and technology event organized by the Indian Institute of Technology Bombay, India announced that it will launch 50 satellites in the next five years.
GS Paper 2: Bilateral, regional and global groupings and agreements
Context:
India is on the brink of securing a significant deal for five lithium blocks in Argentina, with negotiations reportedly in the final stages.
Major Highlights:
The Ministry of Mines, represented by the state-owned Khanij Bidesh India Ltd (KABIL), has initiated a preliminary exploration and development agreement with the Argentinean miner CAMYEN.
This agreement is aimed at the potential acquisition and development of around five lithium blocks.
Additionally, the company has signed a non-disclosure agreement with the Chilean miner ENAMI, exploring opportunities for mineral exploration, extraction, processing, and commercialization.
Furthermore, they have engaged the consultancy firm PwC to identify viable investment projects in Australia.
Acquisitions in Argentina:
GS Paper 2: Government policies and interventions
Context:
Canada-based gangster and Babbar Khalsa International leader Lakhbir Singh Langa has been declared an “individual terrorist" under the Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act.
Details:
In a notification issued by the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA), it stated that Landa was closely associated with Canada-based pro-Khalistan elements including Sikhs for Justice leader Gurpatwant Singh Pannu, and Khalistan Tiger Force leader Hardeep Singh Nijjar among others.
He is the 55th individual to be designated as a terrorist under UAPA.
Though present Canadian Government has not been very supportive in recent times in issues related to Khalistani terrorists.
CHARGES AGAINST LAKHBIR SINGH:
GS Paper 3: Indian Economy and issues relating to planning.
Context:
The government has increased interest rates on two small savings schemes for January-March 2024, making it the sixth consecutive quarterly hike since October- December 2022.
Context:
A total of 57.83 lakh street vendors have benefitted from the PM SVANidhi scheme which was launched during the COVID-19 pandemic to provide affordable loans to hawkers.
Overview:
Around 45% (25.78 lakh) of women street vendors have received loans and 72% of the beneficiaries are from marginalized sections.
The scheme, apart from disbursing substantial loans, has also facilitated digital transactions.
This has not only provided financial assistance but has also expanded the market reach for our street vendors.
PM SVANidhi Scheme:
Context:
PM’s visit to Ayodhya comes ahead of the much-awaited consecration ceremony of the Ram Temple on January 22.
Context:
Litchi is no longer restricted to Muzaffarpur in Bihar, it is now being cultivated across 19 Indian states.
Litchi cultivation for commercial purposes is going on in 19 states.
About Litchi cultivation:
Context:
The triangles, circles and lines in austere white against a mud brown background align to tell stories of village life and the customs and traditions there on walls and canvasses.
About Warli Paintings:
Warli art, originating from the tribal communities of the North Sahyadri Range in Maharashtra, has roots dating back to the 10th century AD.
However, its distinctive style gained recognition and appreciation only in the early 1970s.
Suvasini women from the Warli tribe traditionally practiced this art, adorning the Lagna Chowk, also known as the wedding square.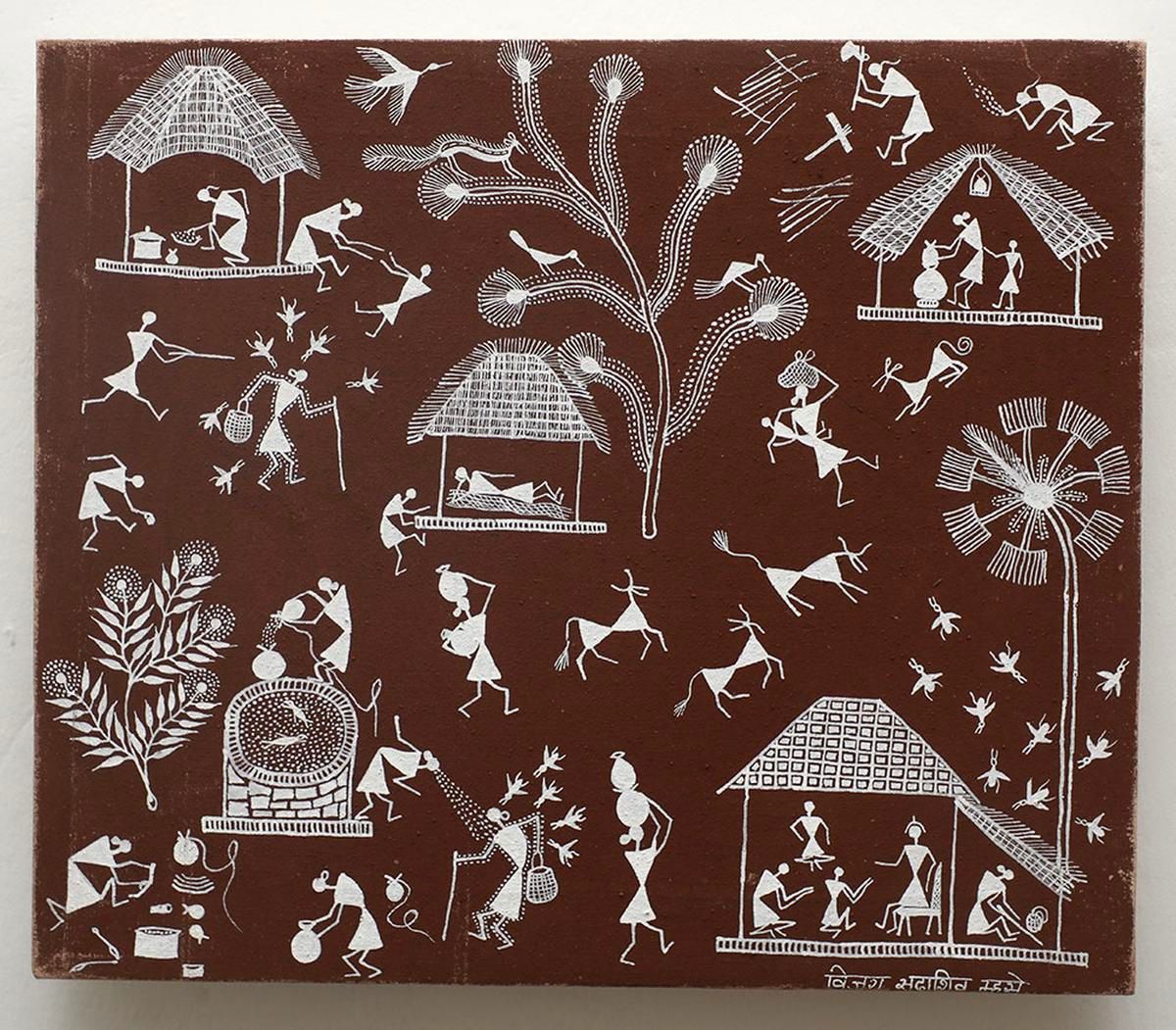
Themes:
Warli art serves as a portrayal of everyday rural life, encapsulating the relationship between tribal communities and nature, their deities, myths, traditions, customs, and celebrations.
Using elementary geometric shapes—circles, triangles, and squares—Warli paintings primarily revolve around the central motif of the square, referred to as "chauk" or "chaukat."
This square often appears in two forms: Devchauk and Lagnachauk.
A prevalent theme within Warli's paintings is the depiction of the tarpa dance, a significant aspect of many compositions.
During this dance, a trumpet-like instrument called tarpa is played in succession by various village men.
Meanwhile, men and women join hands and move in a circular formation around the tarpa player, a scene often depicted in Warli art.
Technique and materials:
Context:
Health Ministry released data on the Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri — Jan Arogya Yojana (AB PM-JAY).
Highlights of Data: