There are no items in your cart
Add More
Add More
| Item Details | Price | ||
|---|---|---|---|
GS Paper 3: Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization of resources, growth, development and employment.
Context:
The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) has proposed the introduction of a facility for clearing and settlement of funds and securities on T+0 (same day) and instant settlement cycle on an optional basis.
SEBI's Proposals:
SEBI proposed introducing a shorter settlement cycle for the equity cash segment, suggesting two phases:
GS Paper 2,3: Health & Pollution
Context:
Used water that goes into the ground, open spaces, into open drains or canals should be channelized into proper Sanitation Systems for public health and environmental preservation.
About Sanitation systems:
Sanitation systems are designed to contain, convey, treat, and either dispose of or reuse the used water (given its value as a resource, the term ‘used water’ is preferred over ‘wastewater’).
It is ensuring good public health and reducing environmental pollution.
While rudimentary sanitation was introduced by ancient civilisations around 4000 BC, the modern sanitation system was built in London around the 1800s.
Types of Sanitation systems:
GS Paper 2: Role of Civil Services
Context:
On the occasion of Good Governance Day, Union Minister Dr Jitendra Singh launched the Extended Version of Mission Karmayogi.
- Three new features launched on the iGOT Karmayogi platform are My iGOT, Blended Programs and Curated Programs.
New features launched on Mission Karmayogi platform:-
The mission seeks to rejuvenate India's bureaucracy, recognizing its pivotal role in the nation's advancement.
It aims to modernize the outdated recruitment and post-recruitment processes for civil servants, aligning them with the evolving needs and aspirations of citizens.
Emphasizing competency-driven capacity building, the program centers on a homegrown Competency Framework tailored for the Indian Civil Services to empower a more effective government workforce.
Other Important Features:-
Context:
The 2023 Chinese Central Economic Work Conference (CEWC) recently concluded, highlighting a stability-focused pathway for the nation’s 2024 economy.
Major Highlights:
Key directives include shifting from export-led to domestic demand-led growth, enhancing high-quality production, striving for tech self-reliance while cooperating with trade partners, and maintaining financial discipline.
This agenda underscores the necessity for structural reforms, requiring a shift away from established Chinese party-state practices to mould the nation's economic trajectory.
How is China strategically addressing the challenges?
Context:
India and Russia signed some “very important” agreements related to the construction of the future power-generating units of the Kudankulam nuclear power plant.
About Kudankulam nuclear power plant-:
Context:
Children suffering from lysosomal storage disorders like Gaucher disease are facing a bleak future as their treatment has been stopped due to the exhaustion of one-time support from the Union Health Ministry.
About the Gaucher disease:
Gaucher disease is an inherited lysosomal storage disorder (LSD) characterized by the accumulation of fatty substances (sphingolipids) in the bone marrow, liver, and spleen.
This buildup weakens bones and enlarges organs, leading to symptoms such as enlarged spleen and liver, eye movement disorders, and yellow spots in the eyes.
There are three types of Gaucher disease:
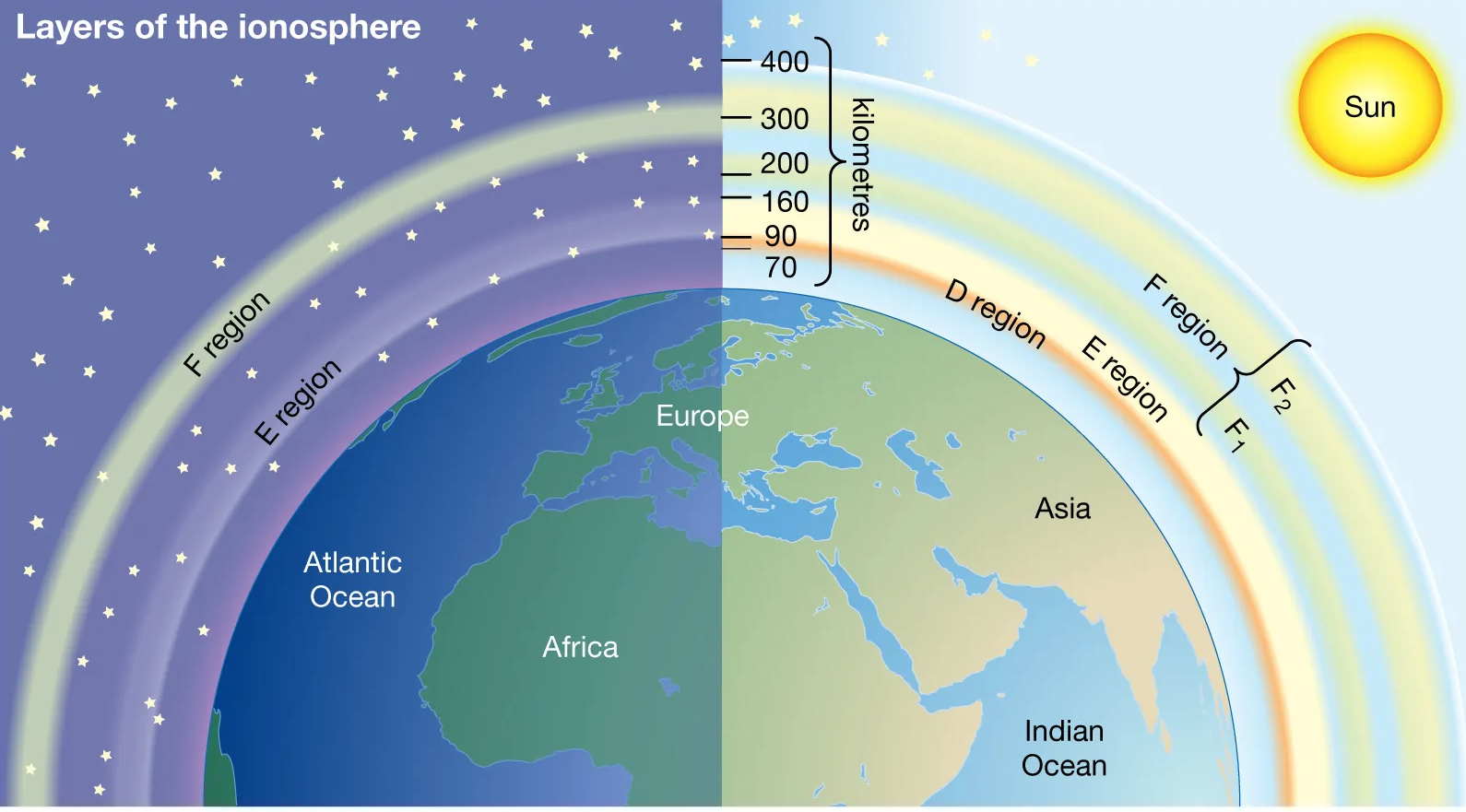
Context:
A team of scientists from the Indian Institute of Geomagnetism (IIG) have examined the long-term seasonal ionospheric observations at Indian Antarctica station Bharati between 2010 and 2022 and also with solar activity following the Sun’s 11-year cycle.
Major Highlights:-
Context:
In a concerning development, scientists are sounding the alarm about the potential spread of a condition known as chronic wasting disease (CWD).