There are no items in your cart
Add More
Add More
| Item Details | Price | ||
|---|---|---|---|
GS Paper 2: Polity and International Relations, Effect of Policies and Polities on India, Important International Institution.
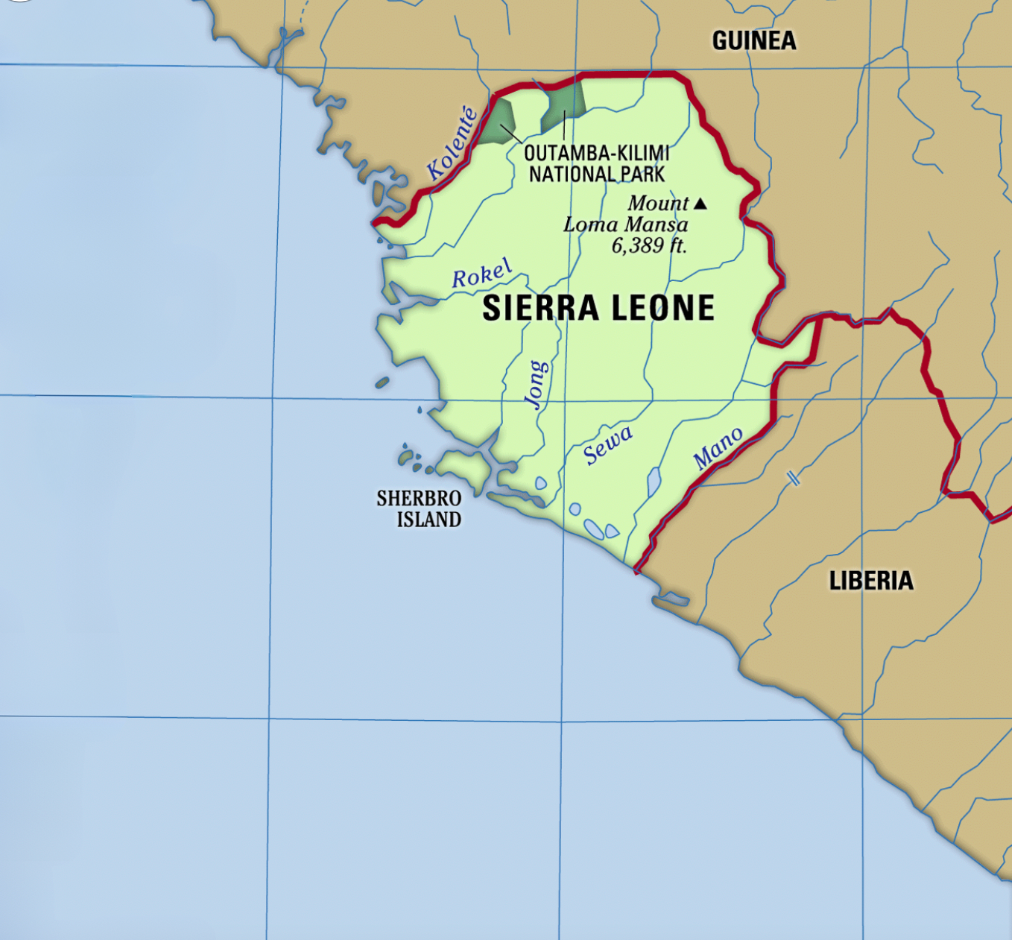
Context-:
Following an assault by unidentified gunmen in the capital, the Minister of Information and Civic Education announced an unsuccessful coup attempt aimed at overthrowing the government.
Details-:
In August 2023, the Sierra Leone police arrested several people, including senior military officers who were accused of planning violent attacks on government institutions.
The recent attacks were an attempt to free the military officers.
An indefinite curfew was immediately levied following the attack and all flights are rescheduled according to curfew.
A cash reward has been declared to anyone who could provide details about the coup leaders.
Factors Contributing to Unrest-:
GS Paper 2: Indian Polity and Constitution; Parliament, State Legislature.
Context-:
A total of 33 Opposition members were suspended from Lok Sabha on Monday for disrupting the proceedings of the House.
Details-:
The current round of suspensions comes after similar action against 14 MPs last week.
The total number of MPs barred from attending the Winter Session now stands at 47 — among the highest ever.
The largest number of MPs suspended from Parliament is from 1989 when 63 lawmakers were asked to walk out.
When are MPs suspended-:
The fundamental principle dictates that it is the responsibility of the Presiding Officer—whether the Speaker of the Lok Sabha or the Chairman of the Rajya Sabha—to uphold order, thereby facilitating the smooth functioning of the House.
To guarantee the proper conduct of proceedings, the Speaker/Chairman possesses the authority to compel a member to withdraw from the House.
How are Lok Sabha MPs suspended-:
GS Paper 3: Achievements of Indians in science & technology and developing new technology
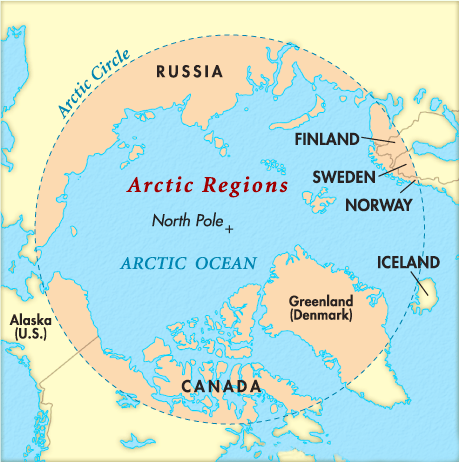
Context:
India will have around-the-year manning of the Arctic with the launch of the first-ever winter expedition in this region.
Context:
The Sultanpur National Park in Farrukhnagar, Gurugram has reported a decrease of 20-30 per cent in the number of migratory birds this season.
Details:
Migratory birds start coming in by the first week of October and around 22,000 birds visit Sultanpur Park every year by the end of January.
This year, it could be much lower.
Reasons:
One of the reasons for this could be the change in temperature level.
The birds come from cold regions like Siberia, Central Asia and Europe.
The decreased migration could be attributable to the fact that the winter is not cold enough to force them out of the region.
If the birds still find food there, they won’t migrate.
There is a disturbance in these smaller wetlands due to increased human activities and interference, and the number of migratory birds here has come down drastically.
Sultanpur National Park:
Formerly recognized as Sultanpur Bird Sanctuary, Sultanpur National Park lies within Haryana's Gurgaon district and primarily comprises wetlands.
This park serves as a crucial habitat for diverse aquatic birds, encompassing both migratory and resident species.
Designated as a Ramsar site in 2021, it holds international significance as a wetland area.
The park showcases tropical and dry deciduous vegetation alongside seasonal aquatic plants and artificial islands.
Additionally, it encompasses open grasslands and features a variety of flora such as grasses, dhok, khair, tendu, ber, jamun, banyan trees, and neem, among others.
The Sultanpur Park has recorded around 250 bird species.
The park with an area of 1.42 sq km, is not only a national park and wildlife sanctuary but also a Ramsar site since 2021.
Context:
Ministry of Mines launched the National Geoscience Data Repository (NGDR) Portal, recently.
About National Geoscience Data Repository Portal:
NGDR is a comprehensive online platform for accessing, sharing, and analyzing geospatial information across the nation.
The NGDR initiative was spearheaded by the Geological Survey of India (GSI) and the Bhaskarachaya Institute of Space Applications and Geoinformatics (BISAG-N).
It represents a significant leap forward in democratizing critical geoscience data, empowering stakeholders across industries and academia with unprecedented access to invaluable resources.
About BISAG-N:
Context:
The Centre introduced the Telecommunications Bill, 2023, in Parliament by the Union minister for Communications, Electronics & Information Technology, recently.
Key highlights of the Bill: