About Civil services
![]()
Civil Services Exam
The Indian Civil Services, encompassing prestigious roles like IAS, IPS, and IFS, stands as the coveted professional journey for countless hopefuls nationwide.
Civil Services as a Career:
The Civil Services form the backbone of the country's administrative machinery. Among the highly sought-after services within this realm are the Indian Administrative Service (IAS), Indian Police Service (IPS), and Indian Foreign Service (IFS). The IAS holds a special allure, as its officers are entrusted with key strategic positions in both Union and State Governments.
Securing a position in these esteemed services involves navigating the rigorous Civil Services Exam (CSE), orchestrated by the Union Public Service Commission (UPSC). This entails successfully manoeuvring through a three-phase selection process, comprising the Civil Services Preliminary Exam (Prelims), the Civil Services (Main) Examination (Mains), and the final frontier, The Personality Test (Interview).
How To Apply?
![]()
Aspiring candidates must submit their applications online through the official UPSC website, i.e.
www.upsconline.nic.in.
•Applicants should diligently fill out the Online Application Form, a two-part process involving Part-I and Part-II, following the instructions provided on the aforementioned website.
•To complete the application process, candidates need to remit a fee of Rs. 100/- (Rupees One Hundred only). However, it's worth noting that SC/ST/Female/Persons with Benchmark Disability candidates are exempt from this fee. Payment can be made by depositing cash in any State Bank of India branch, utilizing the net banking facility of State Bank of India, or employing Visa/Master/RuPay Credit/Debit Cards.
•Prior to commencing the Online Application Form, candidates must ensure their preparedness by having their photograph and signature scanned in jpg format. It's crucial that each file adheres to the specified guidelines, with the photograph ranging between 3 KB and 40 KB, and the signature not less than 1 KB in size. This meticulous preparation ensures a smooth and efficient application process.
•It's advisable for applicants to refrain from submitting multiple applications. In the event of multiple submissions, the Commission will prioritize the application with the higher Registration ID.
•Furthermore, candidates should exercise diligence in providing a valid and active E-Mail ID while completing their Application Form. The Commission may opt for electronic communication at various stages of the examination process, making a functional E-Mail ID crucial for seamless correspondence.
Examination Plan:
![]()
The Civil Services Examination unfolds in two successive stages:
1. Civil Services (Preliminary) Examination: This stage is objective in nature and serves to identify candidates eligible for the Main Examination.
2. Civil Services (Main) Examination: This stage combines a written component and an interview, aiming to select candidates for the diverse Services and posts.
Note:- Once candidates are deemed qualified for the Civil Services (Main) Examination, the next step involves the submission of the Detailed Application Form (DAF).
1st Stage Information (Prelims):
•The Civil Services (Preliminary) Examination is divided into two papers, each carrying 200 marks: General Studies Paper I and General Studies Paper II (CSAT - Civil Service Aptitude Test).
•The GS Paper-II is of qualifying nature, requiring candidates to secure a minimum of 33% marks.
•It consists of objective-type questions (Multiple Choice Questions), and the marks obtained in this stage are considered solely for determining merit in the preliminary examination, not for final selection. Successfully clearing the Prelims is a prerequisite for advancing to the next stage of the examination process.
2nd Stage Information (Mains):
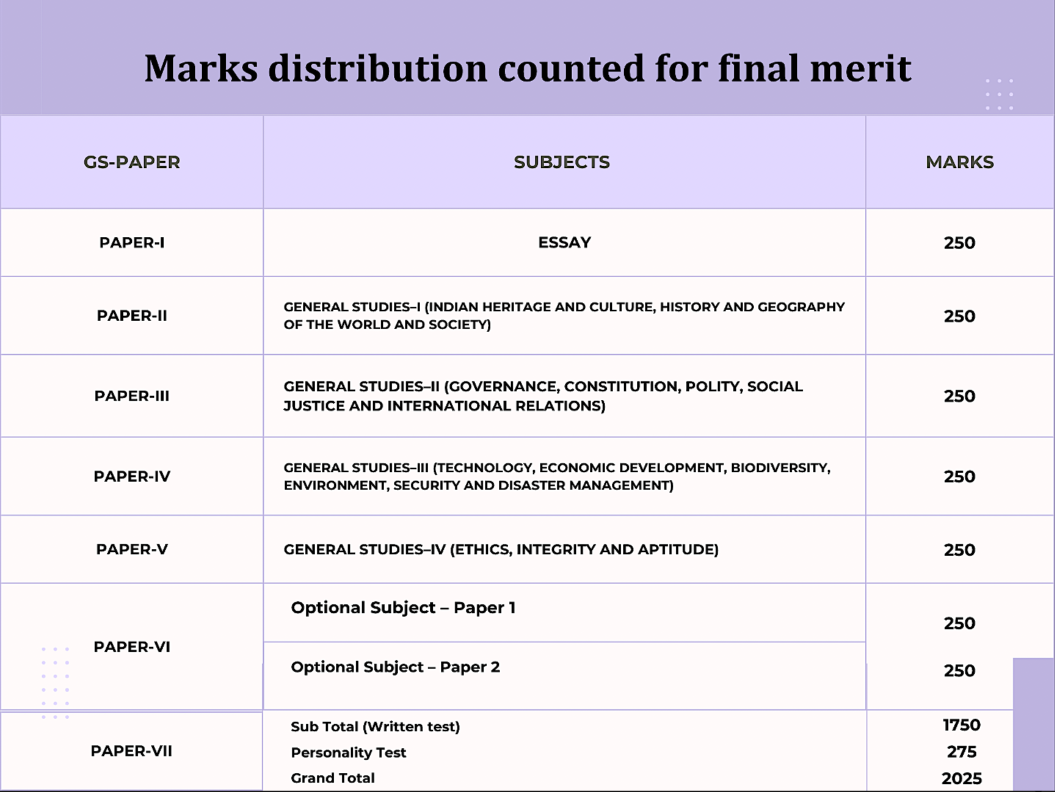
•The Civil Services (Main) Examination marks the 'written stage' of the overall examination process. It comprises nine papers, with the marks of seven papers being considered for the final merit list. For the remaining two papers, candidates must attain the minimum qualifying marks set by UPSC each year. The question papers for the Mains examination are of a conventional (essay) type, adding a subjective element to the evaluation process.
•The Civil Services Personality Test involves a board of members tasked with evaluating the candidate's personality. During this interview, candidates are questioned on matters of general interest. The primary objective is to assess the candidate's personal suitability for a career in public service. The Board, comprised of competent and unbiased observers, aims to gauge the mental caliber of the candidate through this test.
Note:- Final rank of a candidate in merit list is depends upon the marks scored in second stage only i.e. written and Interview.
![]()
Two Qualifying Papers are:
•Paper-A, where candidates need to choose one Indian language from those listed in the Eighth Schedule of the Constitution. This paper carries a weightage of 300 marks.
•Paper-B in English, also valued at 300 marks.
Eligibility Criteria:
![]()
•For the IAS and IPS candidates are required to be citizens of India. However, for other services, eligibility extends to individuals who are either citizens of India or citizens of other countries, subject to specific conditions that need to be met for eligibility. The nuanced eligibility criteria reflect the diverse nature of the Civil Services Examination and the range of services it encompasses.
•Candidates should be between 21 and 32 years old as of August 1 in the examination year. The upper age limit can be relaxed by up to 5 years for SC/ST candidates and 3 years for OBC candidates. Ex-Defense personnel and candidates with specific disabilities also qualify for age relaxation.
•Candidates must have a university degree or an equivalent qualification to be eligible for the Civil Services Examination. Those in the final year of their degree or intending to appear at a qualifying examination are also eligible for the Preliminary Examination. However, they must provide proof of passing the required examination before participating in the Civil Services (Main) Examination.
Note:- A candidate who got appointed as an IAS or IFS officer in earlier examination and continues to be a member of that service will not be eligible to compete at this examination. Moreover, a candidate who is appointed to the Indian Police Service will not be eligible to opt for the Indian Police Service in the next exam.
List of optional subjects for Main Examination:
![]()
(i) Agriculture
(ii) Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Science
(iii) Anthropology
(iv) Botany
(v) Chemistry
(vi) Civil Engineering
(vii) Commerce and Accountancy
(viii) Economics
(ix) Electrical Engineering
(x) Geography
(xi) Geology
(xii) History
(xiii) Law
(xiv) Management
(xv) Mathematics
(xvi) Mechanical Engineering
(xvii) Medical Science
(xviii) Philosophy
(xix) Physics
(xx) Political Science and International Relations
(xxi) Psychology
(xxii) Public Administration
(xxiii) Sociology
(xxiv) Statistics
(xxv) Zoology
(xxvi) Literature of any one of the following languages:
Assamese, Bengali, Bodo, Dogri, Gujarati, Hindi, Kannada, Kashmiri, Konkani, Maithili, Malayalam, Manipuri, Marathi, Nepali, Odia, Punjabi, Sanskrit, Santhali, Sindhi, Tamil, Telugu, Urdu and English.
Other 'Group A' Services:
![]()
•Indian P&T Accounts & Finance Service
•Indian Audit and Accounts Service
•Indian Revenue Service (Customs and Central Excise)
•Indian Defence Accounts Service
•Indian Revenue Service (I.T.)
•Indian Ordnance Factories Service (Assistant Works Manager, Administration)
•Indian Postal Service
•Indian Civil Accounts Service
•Indian Railway Traffic Service
•Indian Railway Accounts Service
•Indian Railway Personnel Service
•Indian Railway Protection Force (Assistant Security Commissioner)
•Indian Defence Estates Service
•Indian Information Service (Junior Grade)
•Indian Trade Service, Group 'A' (Gr. III)
•Indian Corporate Law Service